

Consider, for example, point A, which represents saturated air at 70☏ (DB = WB = DP). To locate lines of constant wet-bulb temperature, at saturation, dry-bulb temperature = dew point temperature = wet bulb temperature, one point on each wet bulb line is already located, that is, the point of intersection of each dry-bulb line with the saturation line. Every engineer, technician, and contractor in the industry should become thoroughly familiar with the psychrometric chart and use it in daily practice. Guidelines for equipment performance can be decided upon, and the limits of any necessary compromises can easily be determined and explained to the customer. With it, the preliminary specifications for an entire system may be laid out.
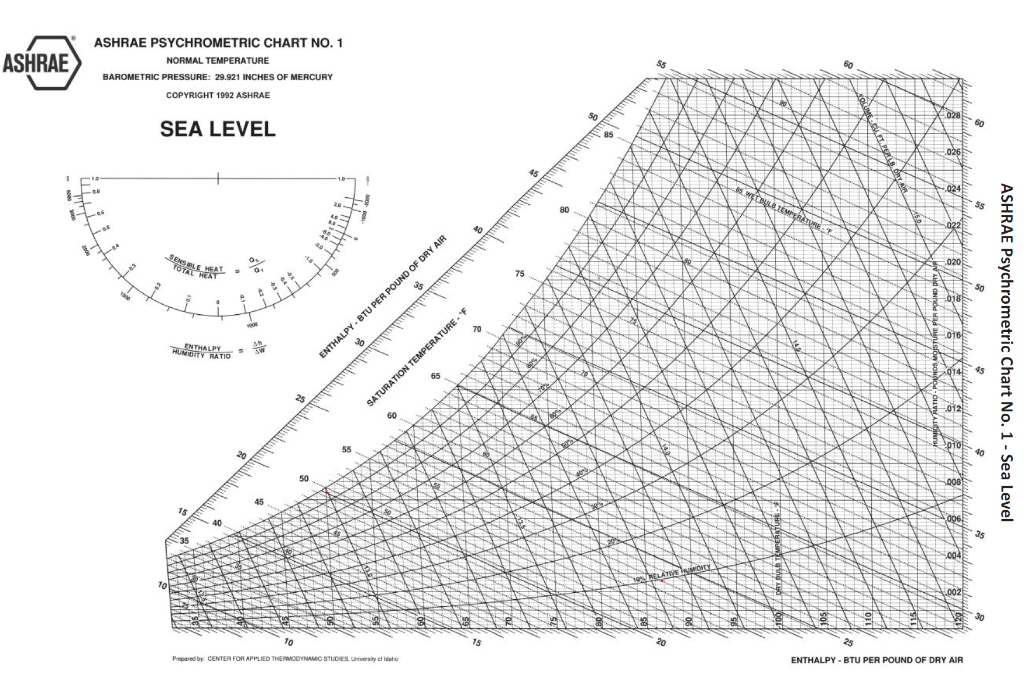

The psychometric chart is probably the most valuable single tool available to the air conditioning engineer or design technician. The one that concerns us here relates temperature, humidity, enthalpy, and certain other properties of moist air is called the Psychrometric chart. Many such charts are used in engineering practice. Air conditioning is not an exact science, and information that is sufficiently precise for the solution of most air conditioning problems can usually be obtained from graphs or charts. Even the use of prepared tables of values is time consuming, since interpolation is often required. Although engineers and technicians need to know how the values of such properties of air as specific humidity, sensible and latent heat, and relative humidity in our designs, the actual computation of these quantities is much too burdensome for everyday operations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
